本文最后更新于:10 个月前
前言
示例代码已经上传到github:点击跳转 点击跳转 点击跳转 gRPC with REST and Open APIs 。
一、gRPC-Gateway概述 1、简述
取自官方概述:
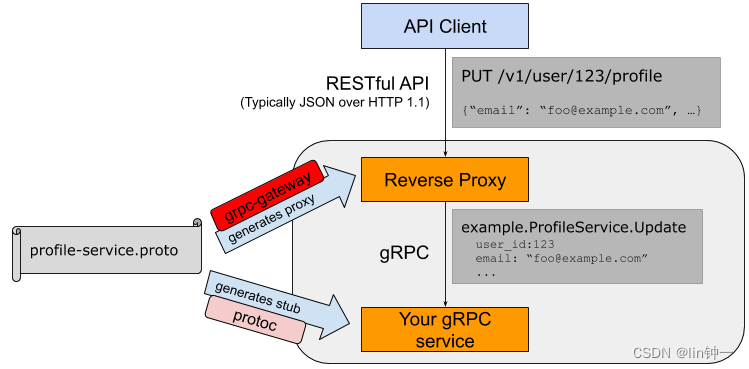
gRPC-Gateway 是 protoc 的插件。它读取gRPC服务定义并生成反向代理服务器,将 RESTful JSON API 转换为 gRPC。该服务器是根据服务定义中的 google.api.http 注释生成的。
2、出现 etcd v3 改用 gRPC 后为了兼容原来的 API,同时要提供 HTTP/JSON 方式的API,为了满足这个需求,要么开发两套 API,要么实现一种转换机制,所以grpc-gateway诞生了。
通过protobuf的自定义option实现了一个网关,服务端同时开启gRPC和HTTP服务。
HTTP服务接收客户端请求后转换为grpc请求数据,获取响应后转为json数据返回给客户端。
当 HTTP 请求到达 gRPC-Gateway 时,它将 JSON 数据解析为 Protobuf 消息。使用解析的 Protobuf 消息发出正常的 Go gRPC 客户端请求。
Go gRPC 客户端将 Protobuf 结构编码为 Protobuf 二进制格式,然后将其发送到 gRPC 服务器。
gRPC 服务器处理请求并以 Protobuf 二进制格式返回响应。
Go gRPC 客户端将其解析为 Protobuf 消息,并将其返回到 gRPC-Gateway,后者将 Protobuf 消息编码为 JSON 并将其返回给原始客户端。
架构如下
二、准备工作 由于本实践偏向 Grpc+Grpc Gateway的方面,我们的需求是同一个服务端支持Rpc和Restful Api,那么就意味着http2、TLS等等的应用,功能方面就是一个服务端能够接受来自grpc和Restful Api的请求并响应。
本文示例代码已经上传到github:点击跳转
1、目录结构 新建grpc-gateway-example文件夹,我们项目的初始目录目录如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 grpc-gateway-example/
certs:存放证书凭证
client:客户端
cmd:存放 cobra 命令模块
pkg:第三方公共模块
proto:protobuf的一些相关文件(含.proto、pb.go、.pb.gw.go),google/api中用于存放annotations.proto、http.proto、google/protobuf中用于存放descriptor.proto
server:服务端
Makefile:用于存放编译的代码。
2、环境准备 1)Protobuf 详细的请移步到《gRPC(二)入门:Protobuf入门》
2)gRPC 详细的请移步到《gRPC(三)基础:gRPC快速入门》
3)gRPC-Gateway gRPC-Gateway 只是一个插件,只需要安装一下就可以了。这里建议科学上网:
1 go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
3、编写 IDL 1)google.api proto 目录中有 google/api 目录,它用到了 google 官方提供的两个 api 描述文件,主要是针对 grpc-gateway 的 http 转换提供支持,定义了 Protocol Buffer 所扩展的 HTTP Option。
2)hello.proto 编写Demo的 .proto 文件,我们在 proto目录下新建 hello.proto 文件,写入文件内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 syntax = "proto3" ;package proto;"./proto/helloworld;helloworld" ;import "proto/google/api/annotations.proto" ;"/hello_world" "*" string referer = 1 ;string message = 1 ;
在 hello.proto 文件中,引用了 google/api/annotations.proto ,达到支持HTTP Option的效果
定义了一个 serviceRPC 服务 HelloWorld,在其内部定义了一个 HTTP Option 的POST方法,HTTP 响应路径为/hello_world。
定义message类型HelloWorldRequest、HelloWorldResponse,用于响应请求和返回结果。
每个方法都必须添加 google.api.http 注解后 gRPC-Gateway 才能生成对应 http 方法。/hello_world 则是请求路径。
3)编译proto 在Makefile文件内输入以下内容:
1 2 protoc:go -grpc_out=. --grpc-gateway_out=. ./proto
Go Plugins 用于生成 .pb.go 文件
gRPC Plugins 用于生成 _grpc.pb.go
gRPC-Gateway 则是 pb.gw.go
使用 make protoc 编译proto:
1 2 ➜ make protocgo -grpc_out=. --grpc-gateway_out=. ./proto
4、制作证书 详细的请移步到《gRPC(五)进阶:通过TLS建立安全连接》
在服务端支持Rpc和Restful Api,需要用到TLS,因此我们要先制作证书
进入certs目录,生成TLS所需的公钥密钥文件
1)生成CA根证书 在 ca.conf 文件并写入内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [ req ]4096 64
生成ca私钥,得到ca.key
1 openssl genrsa -out ca.key 4096
生成ca证书签发请求,得到ca.csr
1 2 3 4 5 6 $ openssl req -new -sha256 -out ca.csr -key ca.key -config ca.conf
生成ca根证书,得到ca.crt
1 openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -in ca.csr -signkey ca.key -out ca.crt
2)生成终端用户证书 在 server.conf 写入以下内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 [ req ]2048 2 letter code)64 .1 = grpc-gateway-example127.0 .0 .1
生成私钥,得到server.key
1 openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
生成证书签发请求,得到server.csr
1 openssl req -new -sha256 -out server.csr -key server.key -config server.conf
这里也一直回车就好。
用CA证书生成终端用户证书,得到server.crt
1 openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -in server.csr -out server.pem -extensions req_ext -extfile server.conf
这样我们需要的证书凭证就足够了
三、命令行模块 cmd 1、Cobra介绍 官方文档:点击跳转
Cobra 是一个用于创建强大的现代 CLI 应用程序的库。它提供了一个简单的界面来创建强大的现代 CLI 界面,类似于 git 和 go 工具。
Cobra 提供:
简易的子命令行模式
完全兼容 POSIX 的命令行模式(包括短版和长版)
嵌套的子命令
全局、本地和级联flags
使用Cobra很容易的生成应用程序和命令,使用 cobra create appname和 cobra add cmdname
提供智能提示
自动生成commands和flags的帮助信息
自动生成详细的 help 信息,如 app -help。
自动识别帮助 flag、 -h,--help。
自动生成应用程序在 bash 下命令自动完成功能。
自动生成应用程序的 man 手册。
命令行别名。
自定义 help 和 usage 信息。
可选的与 viper 的紧密集成。
2、概念 Cobra 建立在命令(commands)、参数(arguments )、选项(flags)的结构之上。
commands :命令代表行为,一般表示 action,即运行的二进制命令服务。同时可以拥有子命令(children commands)arguments :参数代表命令行参数。flags :选项代表对命令行为的改变,即命令行选项。二进制命令的配置参数,可对应配置文件。参数可分为全局参数和子命令参数。
最好的命令行程序在实际使用时,就应该像在读一段优美的语句,能够更加直观的知道如何与用户进行交互。
执行命令行程序应该遵循一般的格式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "linzy"
3、安装 使用 Cobra 很容易。首先,用于go get安装最新版本的库。
1 go get -u github.com/spf13/cobra@latest
4、编写 server 在编写 cmd 时需要先用 server 进行测试关联,因此这一步我们先写 server.go 用于测试
在 server 模块下 新建 server.go 文件,写入测试内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package serverimport ("log" var (string string string string func Serve () error ) {return nil
5、编写 cmd 在cmd模块下 新建 root.go 文件,写入内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package cmdimport ("fmt" "os" "github.com/spf13/cobra" var rootCmd = &cobra.Command{"grpc" ,"Run the gRPC hello-world server" ,func Execute () if err := rootCmd.Execute(); err != nil {-1 )
当前 cmd 目录下继续 新建 server.go 文件,写入内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package cmdimport ("github.com/spf13/cobra" "grpc-gateway-example/server" "log" var serverCmd = &cobra.Command{"server" ,"Run the gRPC hello-world server" ,func (cmd *cobra.Command, args []string ) defer func () if err := recover (); err != nil {"Recover error : %v" , err)func init () "port" , "p" , "50052" , "server port" )"cert-pem" , "" , "./certs/server.pem" , "cert pem path" )"cert-key" , "" , "./certs/server.key" , "cert key path" )"cert-name" , "" , "grpc-gateway-example" , "server's hostname" )
6、启动 & 请求 我们在 grpc-gateway-example 目录下,新建文件main.go,写入内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 package mainimport "grpc-gateway-example/cmd" func main ()
当前目录下执行·go run main.go server·,查看输出是否为(此时应为默认值):
1 2 3 4 5 $ go run main.go server2022 /11 /10 12 :08 :22 50052 2022 /11 /10 12 :08 :22 grpc-gateway-example 2022 /11 /10 12 :08 :22 ./certs/server.pem 2022 /11 /10 12 :08 :22 ./certs/server.key
执行go run main.go server --port=8000 --cert-pem=test-pem --cert-key=test-key --cert-name=test-name,检验命令行参数是否正确:
1 2 3 4 5 $ go run main.go server --port=8000 --cert-pem=test-pem --cert-key=test-key --cert-name=test-name2022 /11 /10 12 :24 :53 8000 2022 /11 /10 12 :24 :54 test-name2022 /11 /10 12 :24 :54 test-pem 2022 /11 /10 12 :24 :54 test-key
到这都无误,我们的 cmd 模块编写就正确了,下面开始我们的重点
7、目录结构 完成以上操作之后我们的目录是这样的结构,看看是不是缺少了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 grpc-gateway-example/go go go go go go
四、服务端模块 server 1、编写 hello.proto 在server目录下新建文件 hello.go ,写入文件内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package serverimport ("context" "grpc-gateway-example/proto/helloworld" type helloService struct {func NewHelloService () return &helloService{}func (h helloService) error ) {return &helloworld.HelloResponse{"hello grpc-gateway" ,nil
2、编写 grpc.go 在 pkg 下新建 util 目录,新建 grpc.go 文件,写入内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 package utilimport ("google.golang.org/grpc" "net/http" "strings" func GrpcHandlerFunc (grpcServer *grpc.Server, otherHandler http.Handler) if otherHandler == nil {return http.HandlerFunc(func (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) return http.HandlerFunc(func (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) if r.ProtoMajor == 2 && strings.Contains(r.Header.Get("Content-Type" ), "application/grpc" ) {else {
GrpcHandlerFunc 函数是用于判断请求是来源于 Rpc 客户端还是 Restful Api 的请求,根据不同的请求注册不同的 ServeHTTP 服务;r.ProtoMajor == 2 也代表着请求必须基于HTTP/2。
如果不需要 TLS 建立安全链接,则可以使用h2c:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 func GrpcHandlerFunc (grpcServer *grpc.Server, otherHandler http.Handler) return h2c.NewHandler(http.HandlerFunc(func (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) if r.ProtoMajor == 2 && strings.Contains(r.Header.Get("Content-Type" ), "application/grpc" ) {else {
3、编写 tls.go 在pkg下的 util 目录下,新建 tls.go 文件,写入内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package utilimport ("crypto/tls" "golang.org/x/net/http2" "io/ioutil" "log" func GetTLSConfig (certPemPath, certKeyPath string ) var certKeyPair *tls.Certificateif err != nil {"TLS KeyPair err: %v\n" , err)return &tls.Config{string {http2.NextProtoTLS},
GetTLSConfig 函数是用于获取TLS配置,在内部,我们读取了 server.key 和 server.pem 这类证书凭证文件。经过一系列处理获取 tls.Config 作为 HTTP2 的使用参数。
4、重新编写核心文件 server/server.go 修改server目录下的server.go文件,该文件是我们服务里的核心文件,写入内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 package serverimport ("context" "crypto/tls" "github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/runtime" "google.golang.org/grpc" "google.golang.org/grpc/credentials" "grpc-gateway-example/pkg/util" "grpc-gateway-example/proto/helloworld" "log" "net" "net/http" var (string string string string string func Serve () error ) {":" + ServerPort"tcp" , EndPoint)if err != nil {"TCP Listen err:%v\n" , err)"gRPC and https listen on: %s\n" , ServerPort)if err = srv.Serve(tls.NewListener(conn, tlsConfig)); err != nil {"ListenAndServe: %v\n" , err)return errfunc createInternalServer (conn net.Listener, tlsConfig *tls.Config) var opts []grpc.ServerOptionif err != nil {"Failed to create server TLS credentials %v" , err)append (opts, grpc.Creds(creds))if err != nil {"Failed to create client TLS credentials %v" , err)if err := helloworld.RegisterHelloHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, gwmux, EndPoint, dopts); err != nil {"Failed to register gw server: %v\n" , err)"/" , gwmux)return &http.Server{
5、server流程刨析 1)启动监听 net.Listen("tcp", EndPoint) 函数用于监听本地网络地址的监听。其函数原型Listen(ctx context.Context, network, address string) (Listener, error)
参数:
network:必须是tcp, tcp4, tcp6, unix或unixpacket。
address:对于TCP网络,如果address参数中的host为空或未指定的IP地址,则会自动返回一个可用的端口或者IP地址。
net.Listen(“tcp”, EndPoint)函数返回值是Listener:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 type Listener interface {error )error
net.Listen 会返回一个监听器的结构体,返回接下来的动作,让其执行下一步的操作,可用执行以下操作Accept、Close、Addr。
2)获取TLSConfig 通过调用 util.GetTLSConfig 函数解析得到 tls.Config,通过传达给 createInternalServer函数完成 http.Server 服务的 TLSConfig 配置项使用。
3)创建内部服务 程序采用HTTP2、HTTPS,需要支持TLS,在启动 grpc.NewServer() 前需要将serverOptions(服务器选项,类似于中间件,可用设置例如凭证、编解码器和保持存活参数等选项。),而前面所获取的 tlsConfig 仅能给HTTP使用,因此第一步我们要创建 grpc 的 TLS 认证凭证。
创建 grpc 的 TLS 认证凭证google.golang.org/grpc/credentials 第三方包,credentials 包实现gRPC库支持的各种凭据,这些凭据封装了客户机与服务器进行身份验证所需的所有状态,并进行各种断言,例如,关于客户机的身份、角色或是否授权进行特定调用。
我们调用 NewServerTLSFromFile 它能够从服务器的输入证书文件和密钥文件构造TLS凭据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 func NewServerTLSFromFile (certFile, keyFile string ) error ) {if err != nil {return nil , errreturn NewTLS(&tls.Config{Certificates: []tls.Certificate{cert}}), nil
grpc ServerOption
grpc.Creds() 其原型为func Creds(c credentials.TransportCredentials) ServerOption,返回一个为服务器连接设置凭据的ServerOption。
创建 grpc 服务端ServerOption
注册grpc服务
1 2
创建 grpc-gateway 关联组件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 if err != nil {"Failed to create client TLS credentials %v" , err)
创建HTTP NewServeMux及注册 grpc-gateway 逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 if err := helloworld.RegisterHelloHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, gwmux, EndPoint, dopts); err != nil {"Failed to register gw server: %v\n" , err)"/" , gwmux)
注册具体服务
1 2 3 4 if err := helloworld.RegisterHelloHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, gwmux, EndPoint, dopts); err != nil {"Failed to register gw server: %v\n" , err)
ctx:上下文
gwmux:grpc-gateway 的请求多路复用器
EndPoint:服务网络地址
dopts:配置好的安全凭据
4)创建Listener 1 2 3 4 5 if err = srv.Serve(tls.NewListener(conn, tlsConfig)); err != nil {"ListenAndServe: %v\n" , err)
5)服务接受请求 我们调用 srv.Serve(tls.NewListener(conn, tlsConfig))它是http.Server的方法,并且需要一个Listener作为参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 func (srv *Server) error {defer l.Close()for {go c.serve(ctx)
它创建了一个 context.Background() 上下文对象,并调用 Listener 的 Accept 方法开始接受请求,在获取到连接数据后使用 newConn 创建连接对象,在最后使用goroutine的方式处理连接请求,完成请求后自动关闭连接。
五、验证功能 1、编写 client 在目录client下,创建 main.go 文件,新增以下内容:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package mainimport ("golang.org/x/net/context" "google.golang.org/grpc" "google.golang.org/grpc/credentials" "grpc-gateway-example/proto/helloworld" "log" func main () "./certs/server.pem" , "grpc-gateway-example" )if err != nil {"Failed to create TLS credentials %v" , err)return ":50052" , grpc.WithTransportCredentials(creds))defer conn.Close()if err != nil {"Grpc" ,if err != nil {
2、启动 & 请求 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # 启动服务端go run main.go server2022 /11 /10 16 :34 :06 gRPC and https listen on: 50052 go run client/main.go 2022 /11 /10 16 :34 :43 message:"hello grpc-gateway"
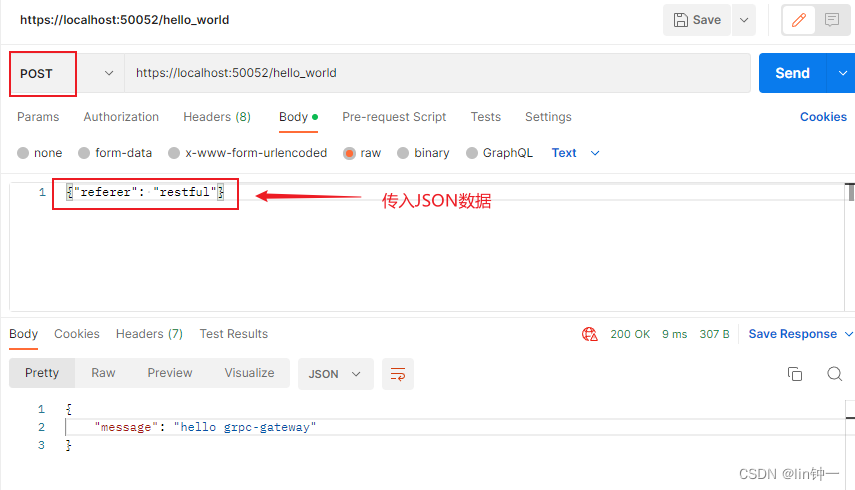
执行测试Restful Api,用POST方式访问https://localhost:50052/hello_world
六、最终目录结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 grpc-gateway-example/go go go go go go go go go go
参考:https://developer.aliyun.com/article/879486 https://eddycjy.com/posts/go/grpc-gateway/2018-02-27-hello-world/